4 stage of predictive maintenance
1. DATA COLLECTION
Obtaining of the maximum possible amount of independent data, valuable for assessing the current state of equipment;
2. DATA PROCESSING
Evaluation of the reliability and consistency of the data,
Elimination of any random components,
Filtration and reduction;
3. DATA ANALYSIS
Multivariate analysis and clustering of the data processed ,
Creation of mathematical models,
Expert analysis;
4. FORECASTING
Choosing a forecasting model,
Forecasting,
Improvement of existing strategies
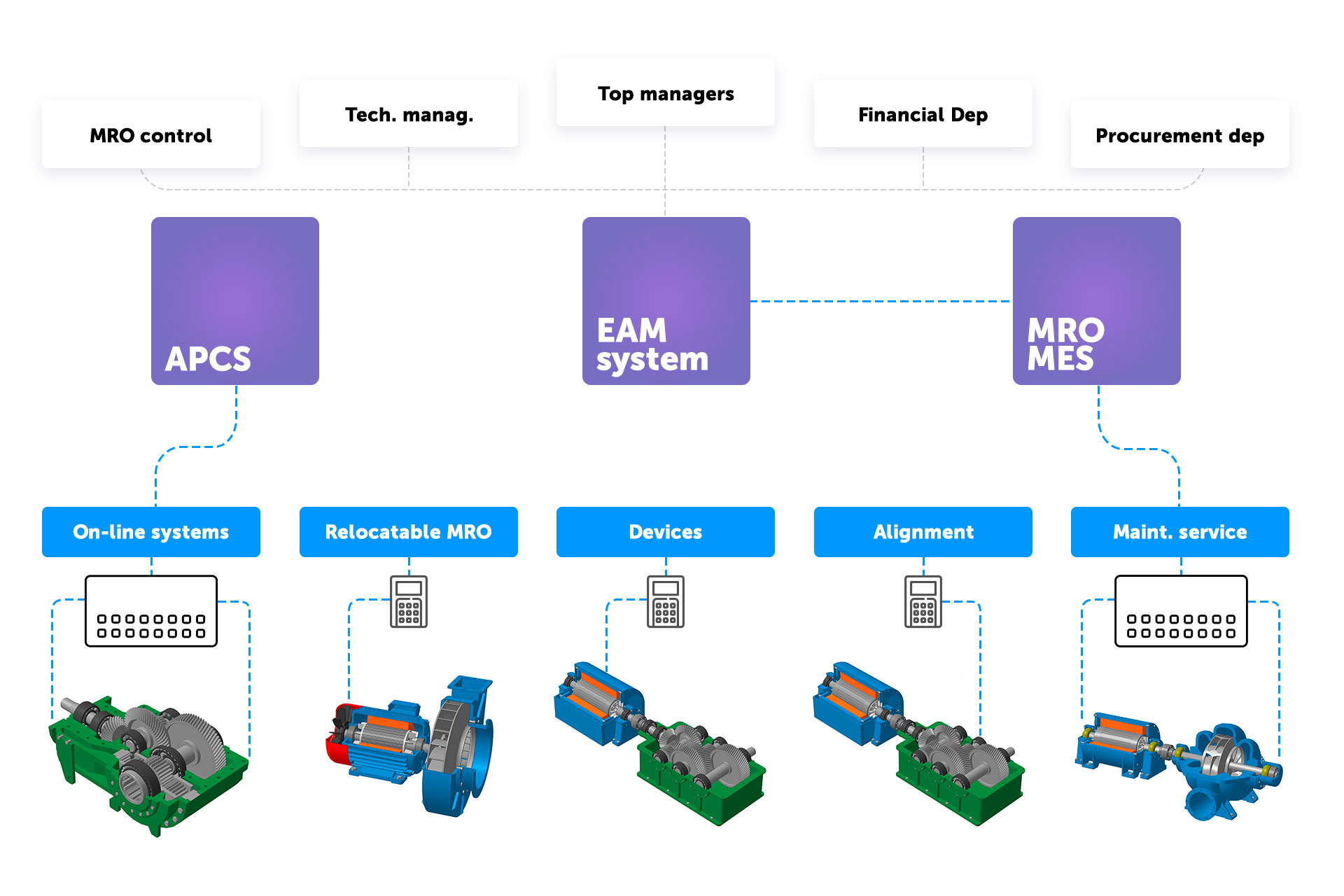
1. Data Collection – Data Sources
APCS and measuring-and-recording apparatus (open protocols):
Various scalar values characterizing the technological process – temperature, rotational speed, current, pressure, etc.;
On-line systems (partly closed protocols):
Various dynamic data characterizing the technical state of the most critical equipment in real time – vibration, temperature, current, mech. quantities, etc.;
PORTABLE DEVICES (completely closed protocols):
Various dynamic data characterizing the technical state of the equipment at predetermined intervals – vibration, temperature-depth profiles, balancing, alignment, etc.;
RELOCATABLE MRO SYSTEM (partly closed protocols):
Various scalar values about the current vibration and temperature, visual control results;
Modules for EAM-systems maintenance (open protocols):
Various scalar values about the MRO activities held, reference books, etc.
2. Data processing – Types of data
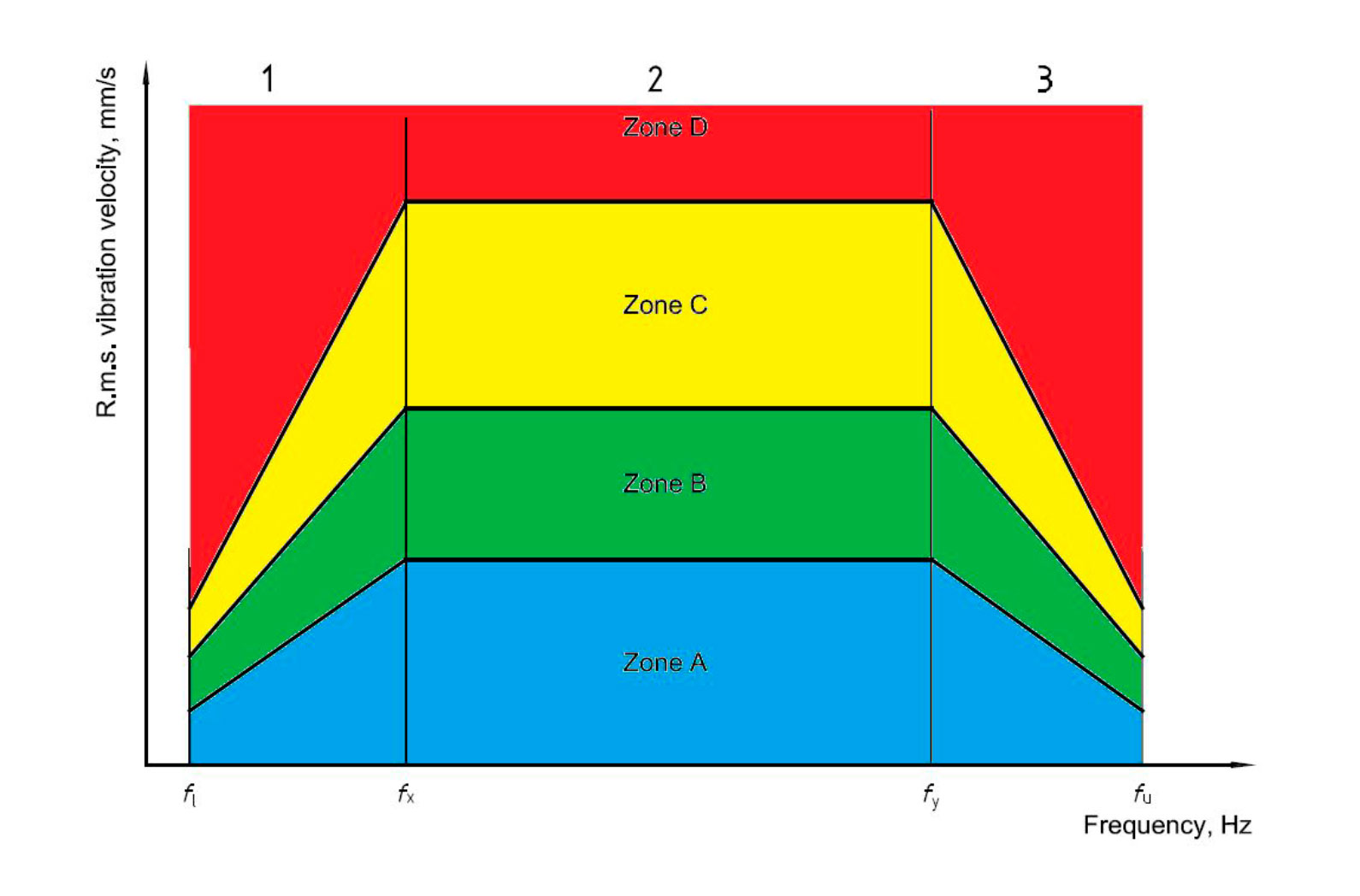
STATE CONTROL
- Assessment of the equipment based on the scale Norm – Warning – Failure in accordance with ISO,
- Enough scalar data (overall vibration, temperature, etc.);
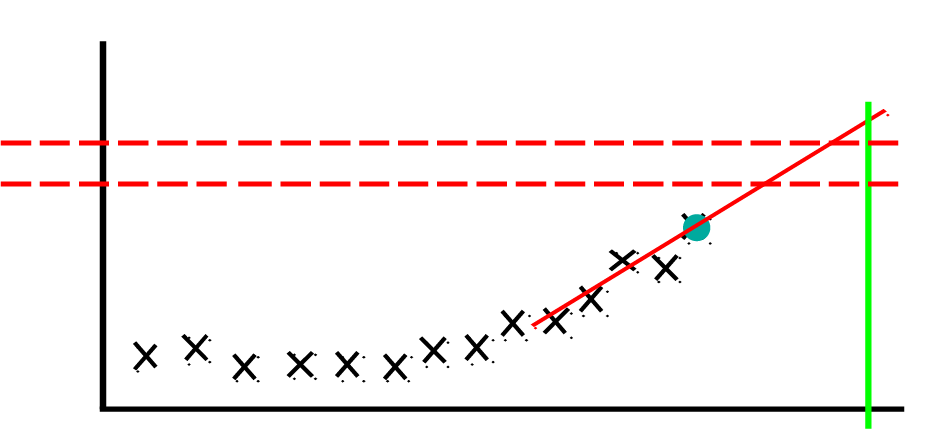
MONITORING (tracking changes over the time)
- Control of change of the scalar parameters over the time according to the results of vibration, temperature measurements, etc.;
DIAGNOSTICS (determination of causes – defects)
- Fault detection using expert systems based on a comprehensive analysis of various types of dynamic data (vibration and current spectra, signal waveforms, temperature-depth profiles, etc.);
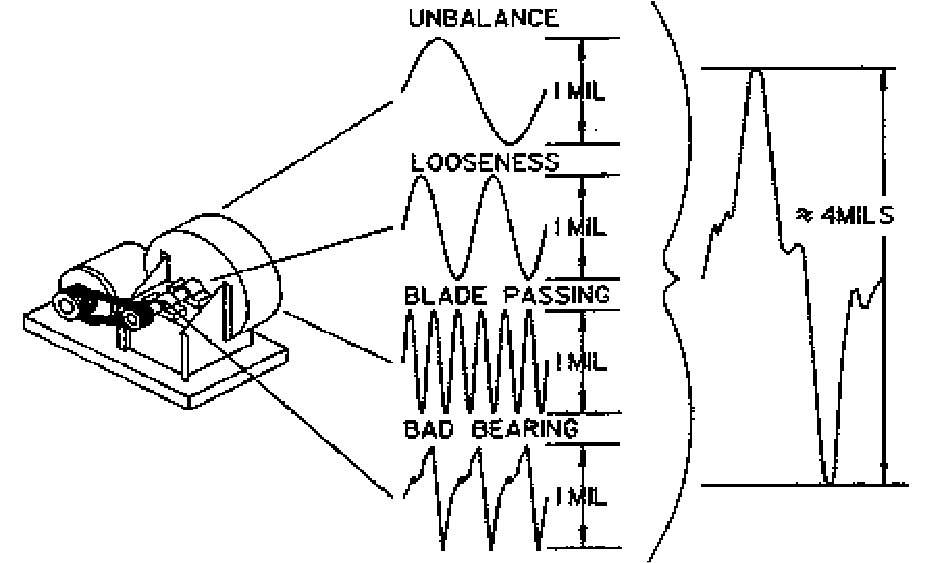
DIAGNOSTIC MONITORING (tracking defects over the time)
- Control of change of dynamic data characterizing faults and forecast of state of reaching the emergency level
3. Data analysis – Object competence
- Knowledge of industry specifics
- Awareness of the technological process
- Studying design specifics
- Analysis of the possible causes of failure
- Selection of diagnostic criteria
- Threshold value calculation
- Study of statistics gathered
- Evaluation of predictive models
- MRO strategies optimization
4. Forecasting– Impact factors

Without due regard to the influencing factors, forecasting and evaluating of the time to reach an emergency state are subject to significant errors, which leads to a significant increase in costs
PROCESS FLOW DEVIATION
Any deviations in the technological process have a significant impact on the rate of malfunction development;
ANTECEDENT MRO ACTIVITIES
Most of MRO activities have a significant impact on the residual operation time;
DIFFERENT FLAW GROWTH SPEED
The residual operation time depends not only on the type of faulty components, but also on the type of defects;
VARIETY OF FAILURE MODELS
Different types of dependencies are specific to different stages of the flaw growth, (different growth rates depending on the current state)


